If you are in manufacturing, or in your company, manufacturing is an important part of the production process, you probably know about additive manufacturing. If not, let me tell you that you are missing out on a technology (or set of technologies) that could greatly speed up the way your company produces, in addition to many other advantages.
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Well, stick around because in this article we’ll tell you what you need to know about additive manufacturing. Is it a good alternative for your company’s specific case? Can it replace other means of manufacturing? We tell you all this and much more in Bitfab.
What is additive manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing refers to the set of technologies that allow the manufacture of objects in a sequential manner, usually layer by layer.
It is defined as additive because the material is added sequentially, as opposed to more traditional (subtractive) manufacturing where material is removed from a solid block until the final part is left. Examples of subtractive manufacturing are turning/lathing, CNC or general cutting processes such as laser cutting, water jet cutting, machine cutting, etc.
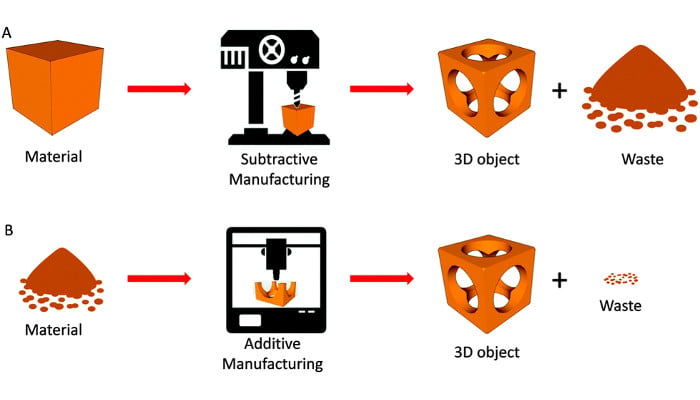
In this way, multiple layers of a material are stacked until they give the definitive form to the object that is being built. The type of material, the height of the layers, the way in which the layers are deposited one on the other can vary.

As you see, although we call it additive manufacturing, we are referring to a very vast world, which actually encompasses extremely diverse technologies.
Perhaps the specific term “additive manufacturing” was unknown until today, but surely this one sounds more familiar to you: 3D printing. Due to the similarity that this process has with paper printing everyone knows, where printing is done line by line until an image is formed, this alternative term has been abandoned and many people call additive manufacturing 3D printing.
Actually, 3D printing as such is only one of the varieties of additive manufacturing, but as a concept it helps us visualize how this family of technologies works and how it can make manufacturing faster and cheaper.
Advantages of additive manufacturing
Well, now that we know what additive manufacturing is, surely you can imagine many advantages that these technologies can have over more conventional means of manufacturing.
Obviously each technology within additive manufacturing has its own advantages over the others, but by sharing a methodology they also share a number of advantages
Reducing the amount of material used
It may be obvious, but by depositing just the right amount of material instead of removing material from a solid block, we do not generate waste. Here is an example of this.

It is a small pawn 25 mm high from a set of chess pieces. Suppose this piece was made by a more traditional technique such as turning a solid block. Assuming the most optimistic ideal case, in which we could use the minimum amount of material we would still have to use a block like the one below.

In this particular case, we would be talking about a material reduction of approximately 70%. This could be further optimized as we could manufacture the part with less than 100% filler so that the amount of material used would be further reduced.

In an extreme case, but perfectly feasible, we could hollow out the piece completely, leaving a “crust” of 1.5 mm. In this case we would have reduced the material used by more than 97% compared to subtractive manufacturing, even though it is an ideal case for this.
Ability to manufacture objects with complex geometries
If you’ve ever designed a part to be made by more traditional means such as CNC, you’ll know that many geometries are literally impossible to make. This is why it is common to divide the part into several smaller parts to avoid complex geometries, requiring a subsequent assembly and increased design and manufacturing time.
Additive manufacturing allows us to make parts that would be practically impossible to achieve with other means, with extremely complex geometries.

Parts such as the one shown above are usually manufactured to demonstrate the technical capabilities of additive manufacturing equipment, making clear their advantage over other means of manufacturing.
Reduced manufacturing cost for small series
While the cost of manufacturing varies greatly depending on which additive manufacturing technology we use, in general the price is significantly lower than with traditional manufacturing.

The graph above shows that the price for short series is lower in additive manufacturing. It is also true that the price practically does not fall with the number of units, as is the case with subtractive manufacturing or injection moulding.
Higher speed and lower prototyping costs
As we have seen in the previous section, additive manufacturing is the cheapest technology when the number of units of a part we want to produce is low. This is why it is ideal for rapid prototyping, where we want to make only one or a few units of a part in order to check for possible failures.
This also fits in with the well-known fast methodologies such as Scrum, where the development of a product requires iterative prototyping until a definitive version is reached.
In addition to being cheaper, it is also more accessible. Additive manufacturing equipment such as 3D FDM printers that we will talk about later, are very cheap to acquire, maintain and operate, so it is viable for almost any company to have its own prototyping workshop, unlike what happens with equipment such as CNC or multi-axis milling machines.
As a summary we leave you with this image, where you can see where the additive manufacturing, and more specifically the 3D printing, is located, compared to other manufacturing models.

To manufacture few and highly complex parts, choosing additive manufacturing will help you save costs, prototype faster and therefore earlier and cheaper in the market.
Additive manufacturing technologies
As we have already told you in the previous sections, there are a lot of technologies that fall into the family of additive manufacturing. We are going to talk about the ones we consider the most interesting, because, given how cutting-edge this field is, there is an almost unlimited variety and we can’t talk about all of them.
The king, 3D FDM printing
3D FDM printing, or molten plastic deposition printing, is currently one of the most (if not the most) widely used technologies in additive manufacturing. This is mainly due to several factors that we are going to explain to you right now.
- Very low initial cost: 3D FDM printers have become extremely affordable in recent years. There are many ranges, but if we go to a professional or semi-professional range we can find alternatives below 1000 euros. Some brands such as Raise3D, Ultimaker or BCN3D manufacture very good quality equipment, with affordable costs for a professional machine and very good after-sales service. Other brands like Prusa are trying to enter this professional market, but we will talk about this a little later.
- Very low cost of materials: As with the machines themselves, the material used, which can range from PLA to nylon or polycarbonates, has reduced its cost while increasing its quality in recent years. That is why, compared to other technologies, not only do we use less material, as we have seen before, but this material is usually quite affordable, which can range from 10 to 80 euros depending on the type of polymer.
- Enormous variety of materials: As we have just told you, the variety of materials is huge. Depending on the application we can look for a cheap, unpretentious polymer such as PLA, or we can need abrasion resistant parts such as PolyCarbonate. If we need a flexible part we can use TPU or TPE, while if what we need is a very light material we can use mixtures with carbon fiber. As you can see the variety is vast. In addition, there are several alternatives such as Palette 2 to make parts that combine several materials
- Ease of use: FDM 3D printers are generally quite easy to use, especially those of the professional range. This makes it possible to have a small production or prototyping centre in the company itself, without the need for specifically qualified personnel.

3D Resin Printers
There are many technologies that pursue the same goal, to print in 3D using photosensitive resin as material. To this end, a multitude of techniques are used, the most widely used being SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) and SLA/DLP (stereolithography).
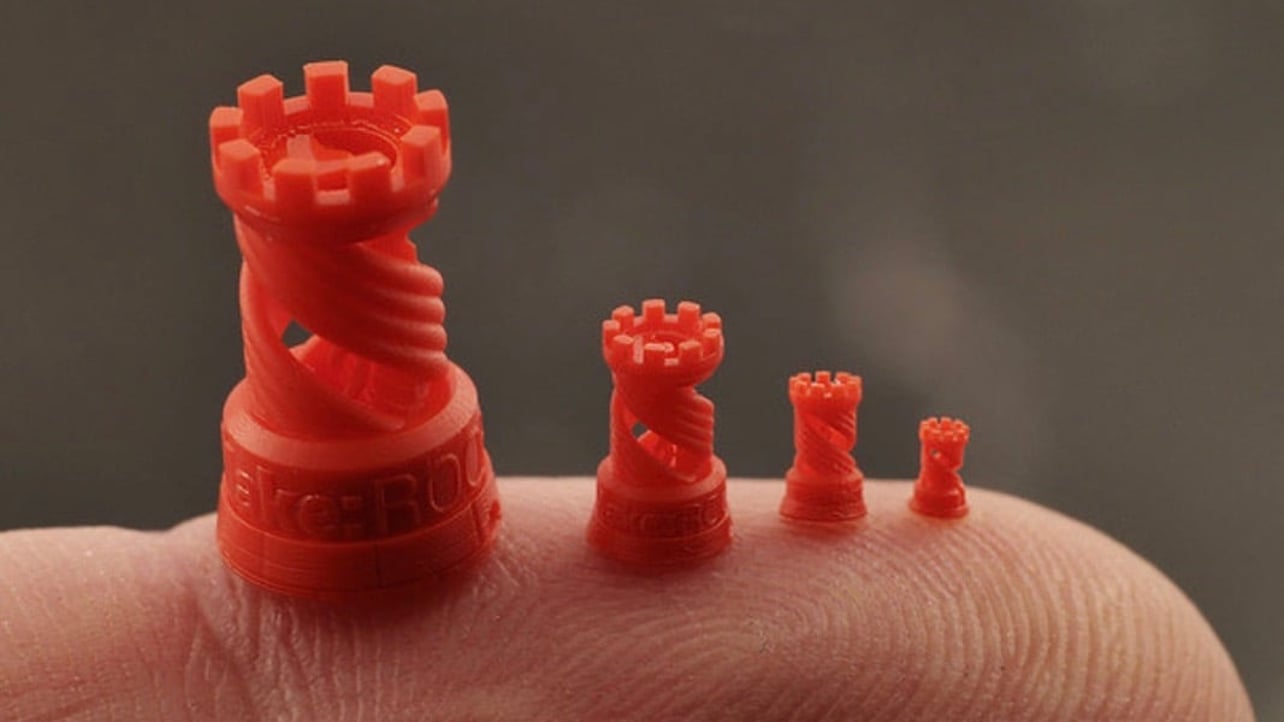
In both cases a light source is used to solidify a photosensitive resin, forming the pieces layer by layer. There are two different technologies, SLA and DLP, which differ in the light source used to polymerise (solidify) the resin. SLA uses a laser and DLP uses a projector or LCD, but the results are similar for most applications.
There are some differences between these technologies, but they generally have the same advantages:
- Very high resolution: While in FDM the resolution in the horizontal axis is usually around 0.5mm and 0.1mm in the vertical axis, resin printers can easily achieve much higher resolutions. Professional printers such as Form 3 by Formlabs achieve a resolution in the XY plane of 0.025mm, or 25 microns, and 0.01mm or 10 microns in the z axis.
- Simplicity of use: These machines operate in a very simple way, and have far fewer moving parts than an FDM printer or other complex piece of machinery such as a lathe or milling machine. Professional printers of this technology are practically plug and play, and require minimal knowledge to operate.
- High speed: Despite printing at a very high resolution, resin printers, especially sterolithography printers. In this respect, new printer models reach amazing speeds of up to one layer per second. We leave you a very interesting video showing a very advanced machine, capable of printing at amazing speeds
While this type of printer has its advantages, it also has some problems that we cannot ignore:
- They’re pretty messy: When working with resin, it’s impossible to avoid making the workshop a messier place. It is possible that, depending on the case of use, you will need a special certificate to be able to host a resin 3D printing workshop, since good ventilation and healthiness must be guaranteed.
- Resin is much more expensive: Resins for 3D printing can be quite expensive, and their price ranges from 50 to 300 euros per kilogram.
Powder Fusion (PBF)
Powder Bed Fusion can be performed through various technologies, as in the previous case. From SLS (again, but sintering powder instead of resin) to electron beam fusion or EBM.

In all these technologies, the aim is to solidify a part from a powder, usually metallic, of materials such as titanium or aluminium. Some of the main reasons for choosing these technologies are:
- Unprecedented design freedom: Usually, when we talk about 3D printing, the environment in which the impression usually occurs is air. This is why, when a portion of our part is not in direct contact with the base, it requires the use of a support structure, since it cannot be printed in the air. This problem does not occur in powder printers (depending on which technology is used), as printing occurs in a chamber filled with this material, so incredible structures can be manufactured without the need for a structure to support bridges or cantilevers.

- Resistance: By using metallic materials, an incredible resistance can be achieved, similar to that obtained by traditional techniques such as CNC.
Other technologies
There are many more technologies, such as jetting, useful for creating full color pieces. We can not talk about all of them in this article, but if you have any specific need, do not hesitate to seek professional help by contacting us in the form that we leave at the end of the article.
Application cases
We’ve told you about a few technologies that can be used to make your production processes faster, cheaper or more efficient, so now we’re going to show you some concrete cases where additive manufacturing can be an amazing advantage.
Rapid prototyping
If you work with fast methodologies in your company, surely you have noticed that many of these technologies can speed up this kind of iterative production models.
3D FDM printing specifically can be incredibly useful as it allows you to quickly produce parts to test their functionality. In particular, in Bitfab we are experts in rapid prototyping using 3D printing, so from our experience we can say that this technology can revolutionize the way many companies work.
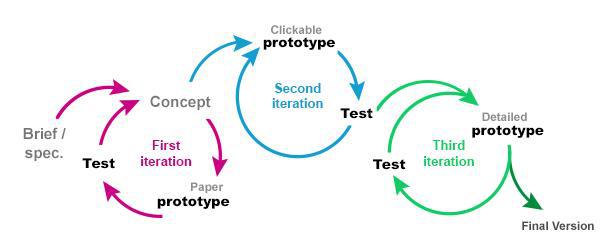
In a matter of days, or even hours if you have your own workshop, you can have a prototype of your model ready, so you can check if it meets the stipulated needs.
Production of final parts
If we are looking for a more rapid and immediate way to produce our final parts, additive manufacturing can be a big boost.
Imagine for example a company that manufactures electronic equipment on demand. This company will need a box or case for its equipment, so a decision is proposed.
On the one hand, they could buy a ready-made box, and adapt the design of the equipment itself to fit this box. This may require moving certain components, redesigning some PCBs or even reinventing some of the equipment. In addition, these boxes probably lack the unique personality you would want to give to your equipment.

On the other hand, you could order the specific manufacture of a box that meets your particular needs in terms of dimensions and appearance. The most common way is to order a mold to make the boxes by plastic injection in this mold. This alternative is usually very expensive, and probably not feasible for short production runs.

With additive manufacturing we can have our small FDM printer farm to manufacture short series of boxes customized down to the millimeter.
The example we give you is a machine that required a series of about 100 units. As you can see, no commercial box would have had the appropriate dimensions or ports for this equipment.
In addition, the flexibility we would have would be enormous, since the box could be adapted to include personalized elements for each client with very little effort. In the example below you can see how we have designed a much more dynamic box than the typical plain box, resulting in a device with its own personality.


Manufacturing on demand
In the case that our company is dedicated to manufacturing goods on demand, additive manufacturing is a great alternative.
Remember that there is a huge amount of technologies, so almost any part you can imagine can be manufactured, even those that would seem impossible for traditional manufacturing technologies either because of their complexity or because of the cost of a single unit.

That’s why additive manufacturing can help us by making that particular, rare piece you need that you can’t find anywhere else.
A good example would be the restoration of old electronic equipment, such as calculators or consoles. Although it may sound strange, there are many companies whose main activity is the restoration of electronic equipment, and one of their biggest headaches is finding original parts of devices that stopped being manufactured decades ago.
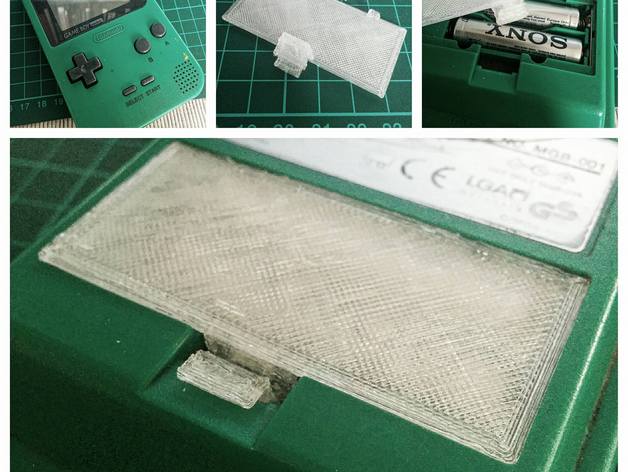
This is where additive manufacturing comes in, since usually the parts that suffer the most in an electronic device are those that are visible, such as the case or buttons. Have you ever tried to find that missing battery cover on the device your customer has asked you to restore? It probably took you a world to find it, and if you did, its price would not be low.
Through additive manufacturing we can make almost any part we can think of, to solve very specific problems that will vary from order to order.
Conclusions
Additive manufacturing is here to stay. We work professionally with almost all manufacturing technologies, additive and subtractive, and so we know that additive manufacturing has many strengths.
As manufacturing professionals, we have tried to show you the types of technologies that are most useful to your business, but if you haven’t found that to be enough, we leave you a contact form. Don’t hesitate to write to us if you need advice on how to take your business to the next level with the help of manufacturing professionals.
